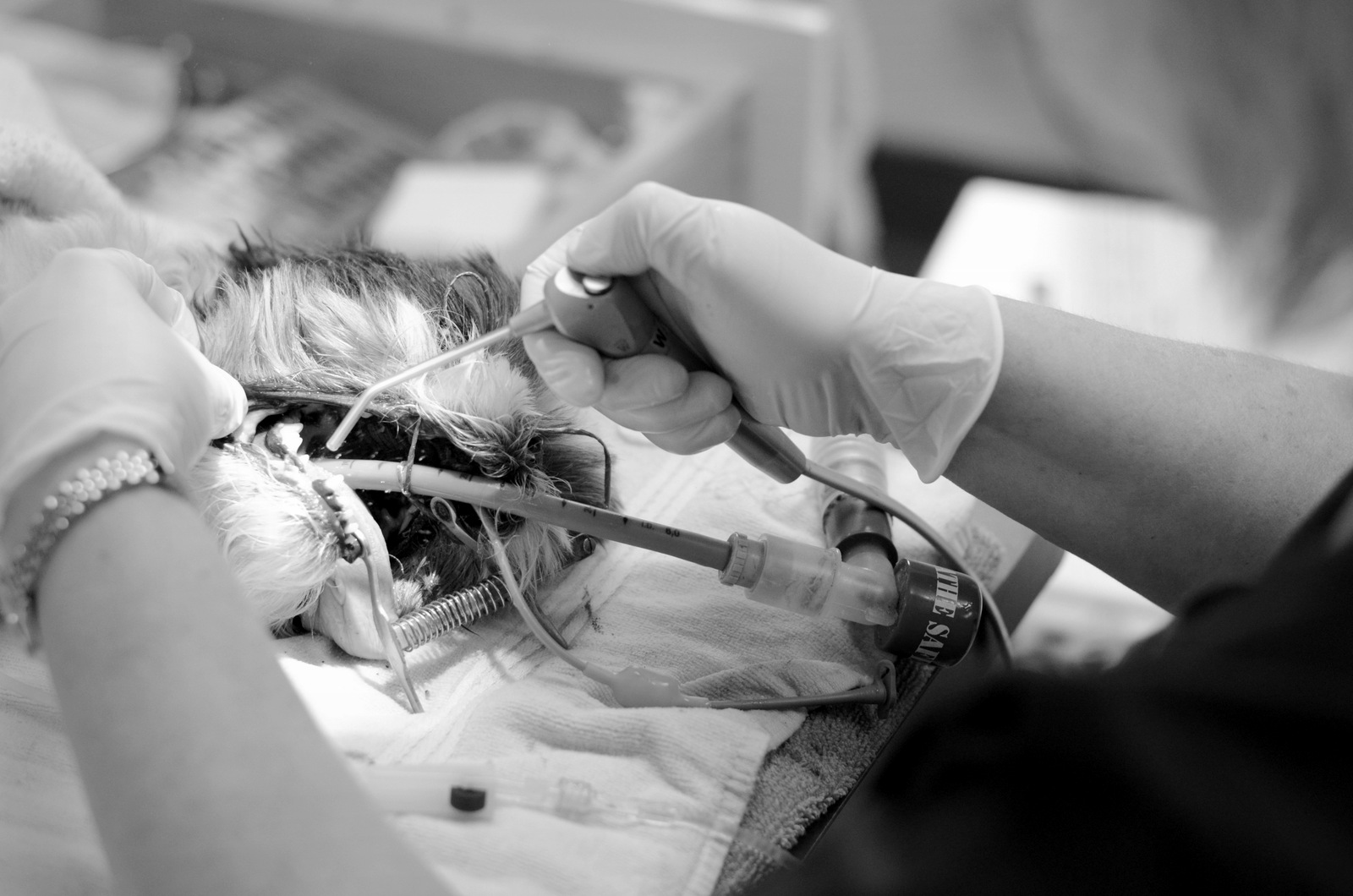
What is a COHAT?
- A general physical examination of the patient, including a thorough assessment of the oral cavity as the patient will allow with identification of oral disease or need for prophylactic care.
- A detailed discussion with the pet owner regarding the need for the procedure and preparation of a treatment plan which outlines associated costs.
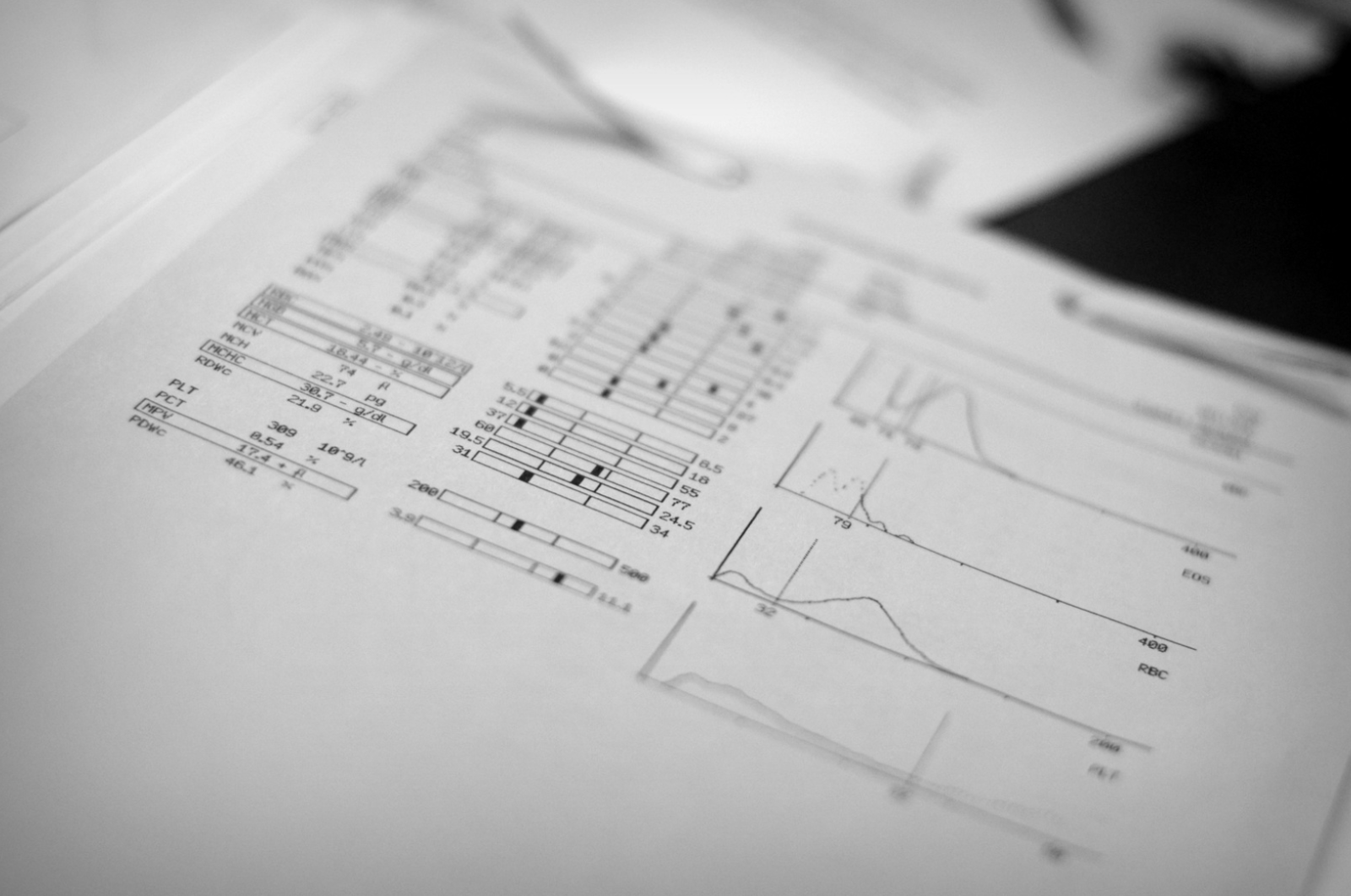
- Pre-anesthetic diagnostic work up including bloodwork, urinalysis, and in some cases, chest x-rays.
- Placement of an intravenous catheter to help facilitate administration of anesthetic induction drugs, and to provide hydration and maintenance of appropriate blood pressure during the procedure.
- Maintenance of anesthesia using inhaled gases, and appropriate monitoring of heart rate, respiratory rate, blood pressure and body temperature.
- Once the patient is anesthetized, a more thorough oral examination can be performed using surgical lighting and magnification looking at the teeth, gums, tongue, cheeks, palette and oropharynx.
- Removal of large chunks of calculus using forceps and/or an ultrasonic scaling device.
- Each tooth is then probed at several points. Abnormal depths and pockets are recorded on a dental chart.


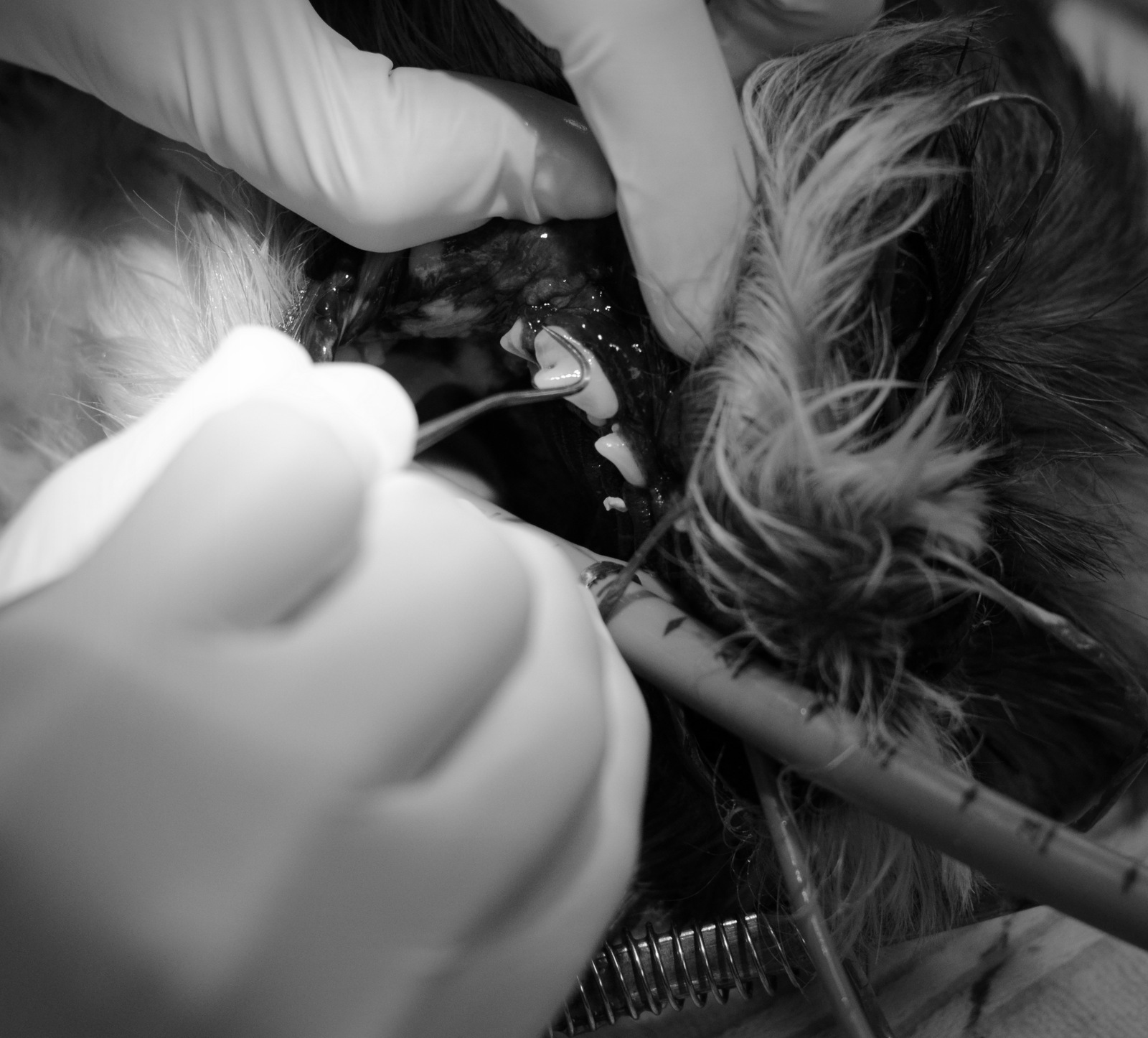
- Crowns (the portion of tooth visible above the gum line) are examined for such damage as discolouration, fractures and abnormal wear.
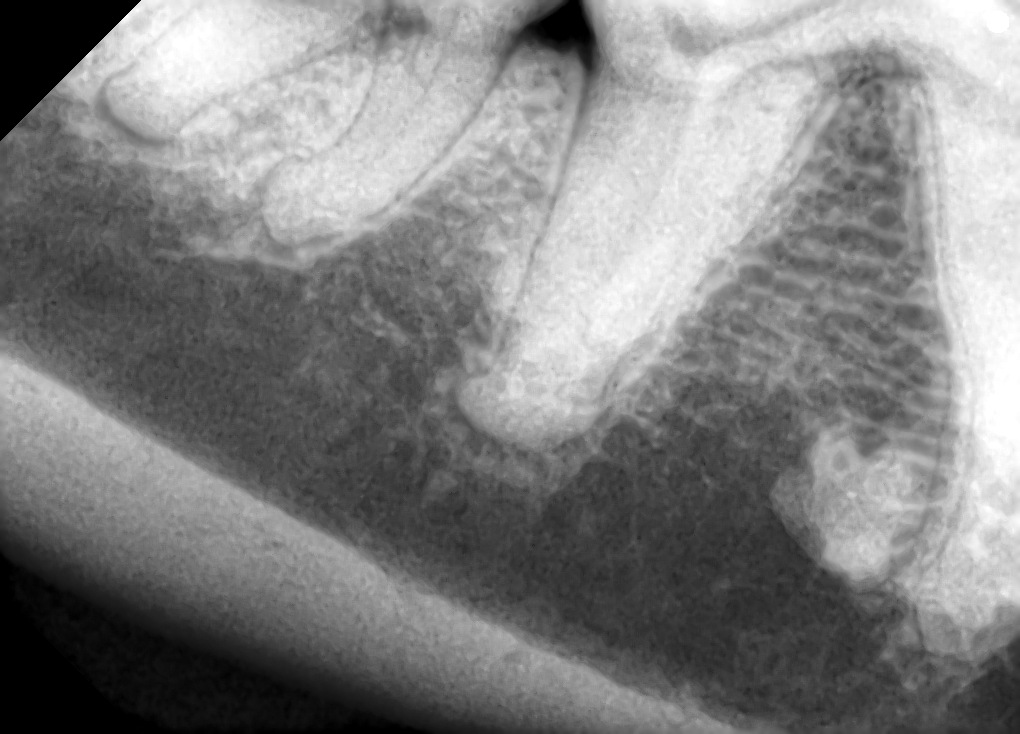
- Whole mouth, intra-oral dental radiographs are taken to allow visualization of the approximately 60% of the tooth (the roots) that is hidden from our view. Intra-oral radiographs also allow assessment of jaw bone integrity and health.
- After clinical and radiographic assessment of the teeth, gingival tissue and surrounding bone, a plan for treatment and correction of any pathology is determined. This is often when we communicate with the pet owner to discuss the treatment plan and make adjustments to the estimated costs.
- All teeth are scaled above and below the gum line using a combination of ultrasonic and hand scaling. This facilitates removal of tartar and calculus that has accumulated.
- All proposed treatments including surgical extraction of diseased or fractured teeth, crown restorations, gingival surgery, wound closure, removal or biopsy of oral masses, etc are now performed. Post-operative radiographs are taken as necessary to confirm root fragments are not left behind following surgical extraction of teeth.
- All remaining teeth are polished above and below the gum line
- The oral cavity is rinsed to remove any blood, calculus or polishing paste and a final, thorough inspection is performed.
- The patient is then recovered from anesthesia. Detailed notes are made on the patient’s dental chart and discharge instructions are prepared for the pet owner.
- A discharge appointment is scheduled with the pet owner. At the discharge appointment, intra oral findings and treatments are explained in detail. Home care instructions outlining immediate care and management, as well as ongoing maintenance of the pet’s oral cavity are reviewed with the pet owner.
- A recheck appointment is scheduled in 10-14 days to assess healing of any extraction sites and/or mass biopsy or removal sites. Ongoing management and preventative care is again reviewed with the pet owner and recommendations for when the next COHAT should be scheduled are made.